NEWS NOT FOUND

Apple cuts China App Store commission fees after government pressure
Apple announced late on Thursday it would lower the commission fees collected in its App Store in mainland China. The move follows pressure from regulators in the tech company’s second-largest market, as well as global scrutiny of its payment requirements.Fees for in-app purchases and paid transactions will be lowered to 25% from 30% starting on Sunday, Apple said in a statement on its blog for developers.“Apple is making changes to the App Store in China following discussions with the Chinese regulator,” the company’s announcement reads. “As of March 15, 2026, changes will be made to the commission rates that apply to the China mainland storefront of the App Store on iOS and iPadOS

Anthropic-Pentagon battle shows how big tech has reversed course on AI and war
The standoff between Anthropic and the Pentagon has forced the tech industry to once again grapple with the question of how its products are used for war – and what lines it will not cross. Amid Silicon Valley’s rightward shift under Donald Trump and the signing of lucrative defense contracts, big tech’s answer is looking very different than it did even less than a decade ago.Anthropic’s feud with the Trump administration escalated three days ago as the AI firm sued the Department of Defense, claiming that the government’s decision to blacklist it from government work violated its first amendment rights. The company and the Pentagon have been locked in a months-long standoff, with Anthropic attempting to prohibit its AI model from being used for domestic mass surveillance or fully autonomous lethal weapons.Anthropic has argued that giving in to the DoD’s demands to permit “any lawful use” of its technology would violate its founding safety principles and open up its technology for potential abuse, staking an ethical boundary that others in the industry must decide whether they want to cross
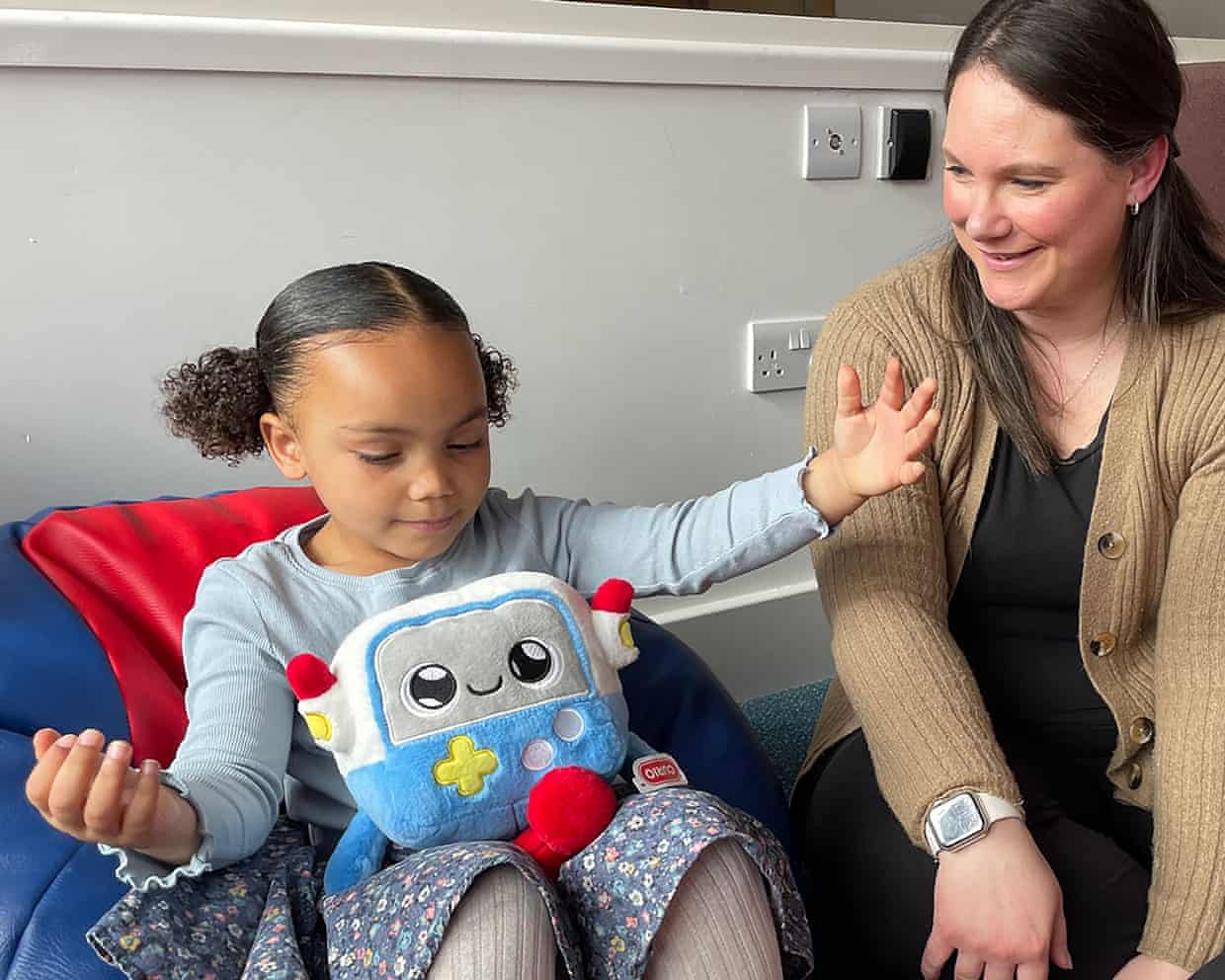

AI toys for young children must be more tightly regulated, say researchers
It was all going well. Charlotte, five, was chatting with an AI soft toy called Gabbo at a London play centre about her family, her drawing of a heart to represent them and what makes her happy. She even offered a couple of kisses to the £80 toy with a face like a computer screen.It was when she declared: “Gabbo, I love you”, that the fluent conversation came to an abrupt halt.“As a friendly reminder, please ensure interactions adhere to the guidelines provided,” said Gabbo, awkwardly crashing into its guardrails

‘IG is a drug’: jury to deliberate as US trial over social media addiction wraps up
The first-ever jury trial over the potential harms of social media wrapped up on Thursday. Lawyers for Meta and YouTube have argued their platforms are safe for the vast majority of young people, while lawyers for a young woman at the center of the case say the tech companies have designed their products to be addictive, leading to mental health issues in children and teens.“How did they become such behemoths?” Mark Lanier, a lawyer for the plaintiffs, said during closing arguments in Los Angeles superior court on Thursday, according to NBC. “It’s the attention economy. They’re making money off capturing your attention
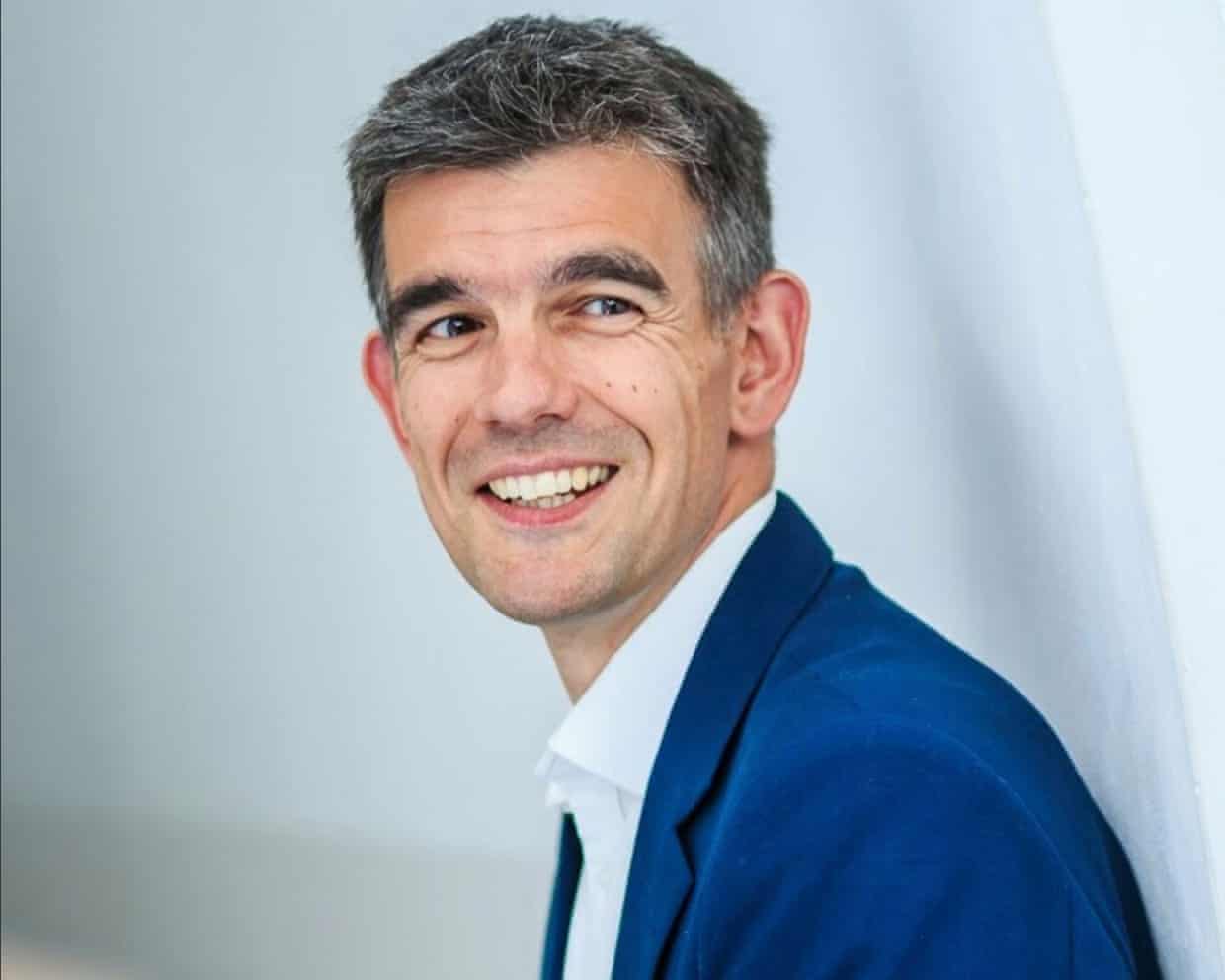

Google’s former Europe boss close to becoming next head of BBC, sources say
Google’s former Europe boss is closing in on becoming the BBC’s next director general, the Guardian has been told.Sources said that Matt Brittin, 57, was very advanced in the appointment process. Some insiders believe that, barring a last-minute development, he will succeed Tim Davie as the broadcaster’s next director general.Brittin, a member of the British Olympic rowing team in 1988, led Google in Europe, the Middle East and Africa for a decade until stepping down last year to take what he described as a “mini gap year”. He is also a non-executive director of Guardian Media Group
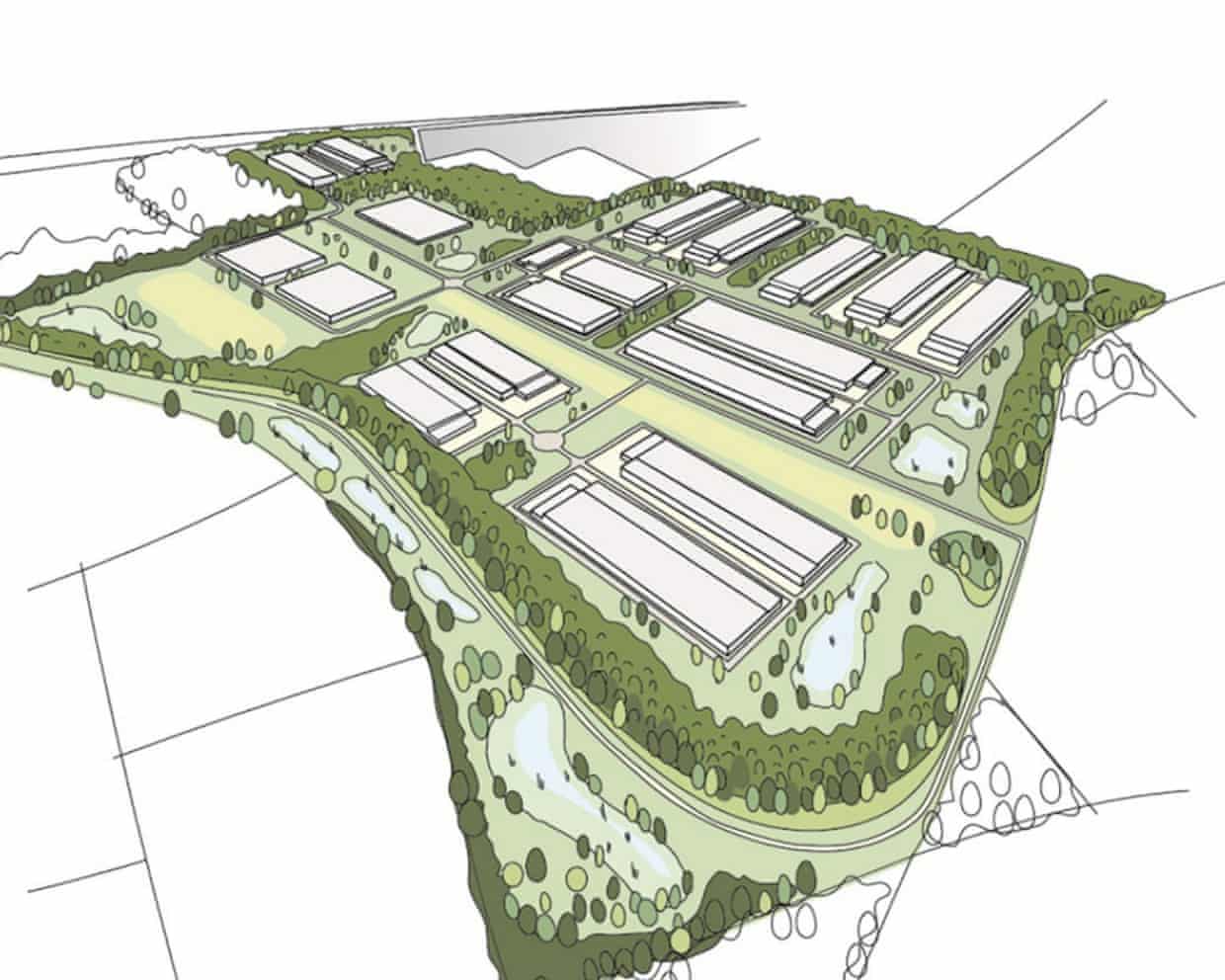
Lincolnshire council approves AI datacentre despite emissions warnings
Plans for a new datacentre in Lincolnshire have been approved, despite warnings it could be a major new source of emissions.On Wednesday, North Lincolnshire council voted unanimously to approve planning permission for the Elsham Tech Park, a proposed AI datacentre campus near Scunthorpe, next to the Elsham Wolds industrial estate.According to the tech justice nonprofit Foxglove, the projected emissions produced will approach those generated by every domestic flight taken in the UK.Council documents estimate the proposed datacentre’s “peak annual scope 2 emissions”, or indirect greenhouse gases from generating electricity, will reach about 1m tonnes of CO2 equivalent in 2033-34. All of the UK’s domestic flights total 1

Patients face long journeys for medicines as pharmacies cut weekend hours

Hundreds of thousands of NHS staff in England attacked and harassed, survey shows

‘Nowhere near enough’ being done to tackle misogyny among young boys

Threats against female MPs having ‘chilling effect’ on women in public life, minister says
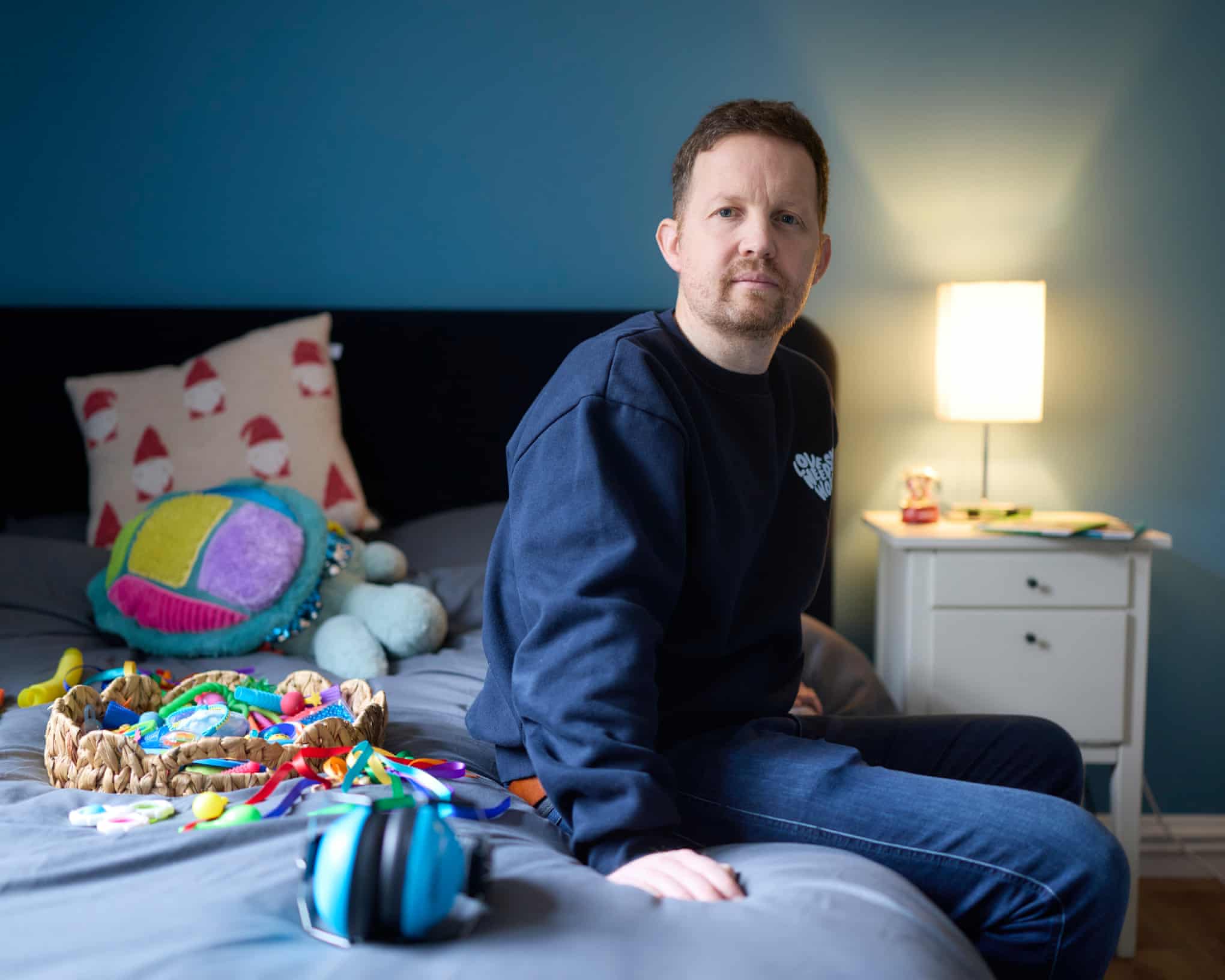

Life with my autistic sons: ‘How do you explain all the worries, the sleepless nights?’

Proposed law change will protect abusive men who push women to suicide, campaigners warn